Travel
Philippines as the country with the world’s largest bats
“The Philippines has 79 recorded bat species, half of them endemic,” explains Dr. Mariano Roy Duya of the University of the Philippines Institute of Biology (UPIB). North America, with a land area that is 66 times larger – has but 45. We have an incredible diversity of bats since each of our 7100 islands is geographically unique. And of course, we have the largest bat of all.”

By Gregg Yan
Did you know that the largest bat of all is found only in the Philippines? Planet Earth has 1400 known bat species and the Golden-crowned Flying Fox (Acerodon jubatus) earns the top spot for size and weight. Known locally as kabog, it is endemic or found nowhere else but in the Philippines.
Strikingly patterned with a golden cap, reddish fur and chocolate-brown wings, adults weigh over a kilogram and can boast of a wingspan nearly two meters across – longer than most people are tall.
“The Philippines has 79 recorded bat species, half of them endemic,” explains Dr. Mariano Roy Duya of the University of the Philippines Institute of Biology (UPIB). North America, with a land area that is 66 times larger – has but 45. We have an incredible diversity of bats since each of our 7100 islands is geographically unique. And of course, we have the largest bat of all.”
Once widespread throughout undisturbed lowland forests across the country, hunting and deforestation – particularly from slash-and-burn upland farming or kaingin – have whittled down bat populations.
Dumaguete-based filmmaker Rhiyad Maturan and I were recently invited by the Energy Development Corporation (EDC) to film a thriving kabog colony inside the Bacon-Manito Geothermal Project, a heavily forested geothermal reservation nestled between the provinces of Albay and Sorsogon on the island of Luzon. Though the area is now verdant and alive, it wasn’t always so.

“Believe it or not, that entire mountain range was once logged-over,” says Ed Jimenez, corporate relations head for EDC’s Bacon-Manito Geothermal Project, pointing at well-forested hills nearby. “The only trees left were the ones loggers ignored. To bring the mountains back to life, we worked with the local communities to help reforest this area while providing them with an alternative source of income. Decades later, the organizations we helped form, like the Alliance of Bacman Farmer’s Association Inc. Agriculture Cooperative (formerly ALBAFAI) and the Bacman Host Community Multi-purpose Cooperative (BMPC), have become some of our most passionate champions. Even the grandchildren of the original members are helping us plant trees, promote community-based conservation and protect these forests.”
Aside from bats, Bicol’s forests also shelter wild deer, pigs, monkeys and birds – most of which were driven to remote areas by decades of hunting and forest loss.
“I learned to shoot kabog with an airgun when I was still a kid,” recalls Joseph ‘Doy’ Gabion, a former bat hunter. “Bats are easy to hunt by day because they hang upside down from their roosts. When the roosts were eventually protected by EDC and its conservation partners, we hunters had to wait until the bats flew out to their feeding grounds. Back in the 1990s, my uncle and I would wait for them to pass to be able to catch two or three bats a night. Kabog meat has a slightly woody taste.” Doy has since stopped hunting and now volunteers with the Armed Forces of the Philippines’ CAFGU Active Auxiliary Unit II to help protect the very animals he once hunted.
The kabog colony moves from one area to another within the Bacman reservation and we chanced upon them roosting on a grove of pine-like Agoho (Casuarina spp.) trees. “We have about 700 kabog individuals here now, our flagship fauna species for this site,” explains Forester Neil Miras, EDC Bacman’s watershed management officer.
Representing iconic wildlife found in its geothermal, solar and wind sites, EDC’s Flagship Species Initiative (FSI) aims to popularize some of the nation’s lesser-known forest denizens. The eight other flagship species include the Philippine Warty Pig (Sus philippensis), Visayan Hornbill (Penelopides panini), Apo Myna (Goodfellowia miranda), plus native trees like Mapilig (Xanthostemon bracteatus), Katmon Bayani (Dillenia megalantha), Red Lauan (Shorea negrosensis),Almaciga (Agathis philippinensis)andIgem-dagat (Podocarpus costalis). EDC has been planting native trees across the country since the 1980s.
“Though millions of trees have been planted under the BINHI Program, we should still recognize the importance and effectiveness of natural seed dispersion – either by the wind, water or by local wildlife,” explainsForester Abegail Gatdula, EDC-FSI project manager. “Flying animals like birds and bats eat the fruits of various forest trees and disperse them far and wide within life-giving guano bombs, giving the seeds a vital headstart.”
Though not as popular as the Tamaraw or Philippine Eagle, the kabog has been quietly doing its part to make the Philippines greener. “Think of them as the ‘silent seed planters’ of nature. We never pay them but they keep working for our world,” concludes Jean Dayap, Municipal Environment and Natural Resources Officer (MENRO) of Manito in Albay.

So tonight, please look up at the night sky to thank our uncelebrated wildlife heroes, quietly working the night shift to make the Philippines a little greener – one guano bomb at a time.
Watch our Golden-crowned Flying Fox documentary HERE.
Destinations
Checking out Street Halo-Halo Milky Ice
#LGBT checking a #halohalo ‘specialist’ in #Manila to compare it with #Chowking, #Razons, and those from #streetvendors.

Tag-init, for many Filipinos, means finding the perfect halo-halo. You can just grab one from those street vendors; almost always, they’re the best. But for those without access to those off-the-street halo-halo vendors, the next best versions would be those from supposed halo-halo specialists… such as Street Halo-Halo Milky Ice, which – like Icebergs and Razon’s – eyes to be known for giving this Pinoy dessert a twist.
@outragemag #LGBT checking a #halohalo ‘specialist’ in #Manila to compare it with #Chowking, #Razons, and those from #streetvendors ♬ original sound – Outrage Magazine
Kumusta naman ang experience sa Street Halo-Halo Milky Ice?










Una, this biz actually has sit-down venues – e.g. the one we checked in Santa Ana in the City of Manila. But exactly because they have to pay for a dining venue, they don’t just offer halo-halo, but also so-so Mexican food. At least the space isn’t bad naman, and allows you to enjoy your halo-halo away from the humidity outside.
Ikalawa, slight maingay ang staff – e.g. when taking orders from foodpanda, or when chatting with each other. Promise, disturbing siya.
Ikatlo, kumusta ang halo-halo and the Mexican snack? More particularly, we tried the ₱150 ube halo-halo and the ₱200 taco?
- With the halo-halo, the winning element is supposed to be the shaved ice since timplado na, so may additional lasa. However… the shaved ice used here may not be lumpy as the one in Chowking, but it not as smooth as Razon’s either.
- If eating at Razon’s, you know there’s not a lot of sahog. But here, even if you do get more, nothing was memorable.
- Lasa-wise, the halo-halo was quite bland… even with all the sahog and all.
- The three pieces of tacos were so-so, tasting more like some inuman venue’s beef nachos than anything else. Overloaded with fake-tasting cheese, this appears like someone’s false idea of what Mexican food really is.
If, in the past, we craved for halo-halo during summer when the heat becomes intolerable, nowadays, that halo-halo craving is now what’s normal. Climate change is real, for real. So Street Halo-Halo Milky Ice has a captured market na. But if you can find others pa rin… like those selling halo-halo in street corners, try them as well. You’re bound to be pleased more for less the price.
So off we go for more lafang venue search…
Street Halo-Halo Milky Ice is located at 2241 Syquia St., Santa Ana, City of Manila, Metro Manila.
Travel
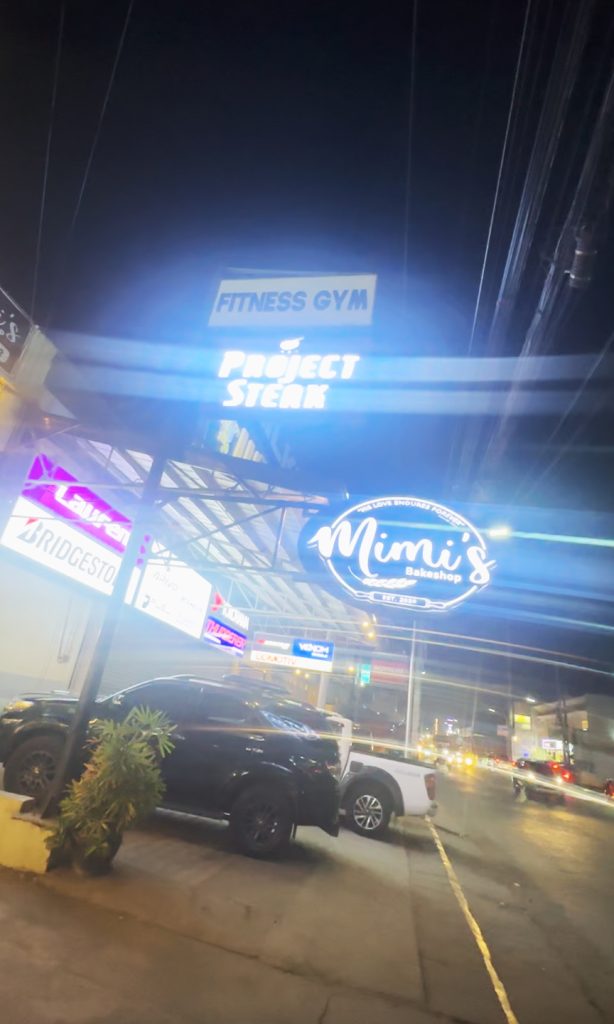
Steak-hunting in Bulacan? We ended up in Project Steak
Attraction-wise, #Bulacan isn’t on top of tourists’ lists. But food-wise, it – surprisingly – has a handful of worthy offerings. We checked one, a #steakhouse comparable to those in Metro Manila.

Bulacan may be a big province, but tourists will – admittedly – have a harder time looking for places to visit here. Unless you’re into hard-to-reach natural wonders, or churches, churches, and even more churches.
There’s something surprising in Bulacan, though: that is, there are actually a lot of not-bad dining venues there… which was what led us to discovering Project Steak.
How was the place for us?
@outragemag Lost in #Bulacan and looking for okay #food? We checked the #steak #fishandchips of @projectsteakbaliwag in #baliuagbulacan for this #LGBT ♬ original sound – Outrage Magazine
Una, Bulacan is a big province, so if you’re nowhere near Baliuag, you may find this place too hard to go to (particularly if you’re not driving). This is over an hour away from the City of Manila, passing through Obando, Bocaue, Guiguinto, Malolos, Pulilan, et cetera… so yeah, this isn’t the most accessible place to go to.
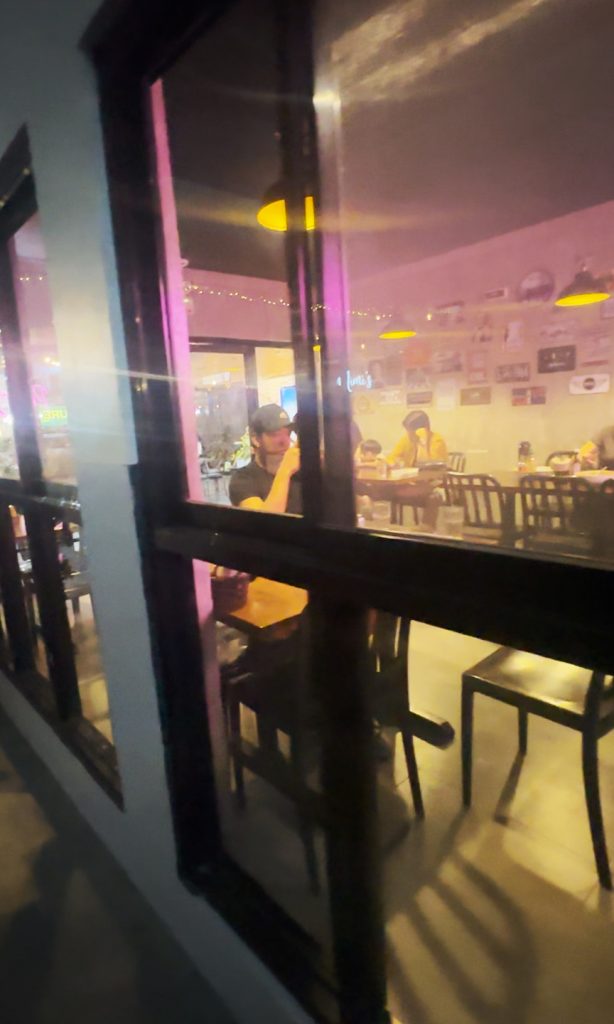
Ikalawa, the actual resto is actually small; seriously small. Luckily, there are two seating areas, so to speak. The resto itself has an airconditioned room that can only seat a handful; and a non-airconditioned area that it shares with Mimi’s, the café beside it. The airconditioning isn’t that cold naman, so staying outside may make sense particularly for those who are claustrophobic.
Ikatlo, keri naman ang personnel, able to explain what’s on the menu.
Ika-apat, how was the food?
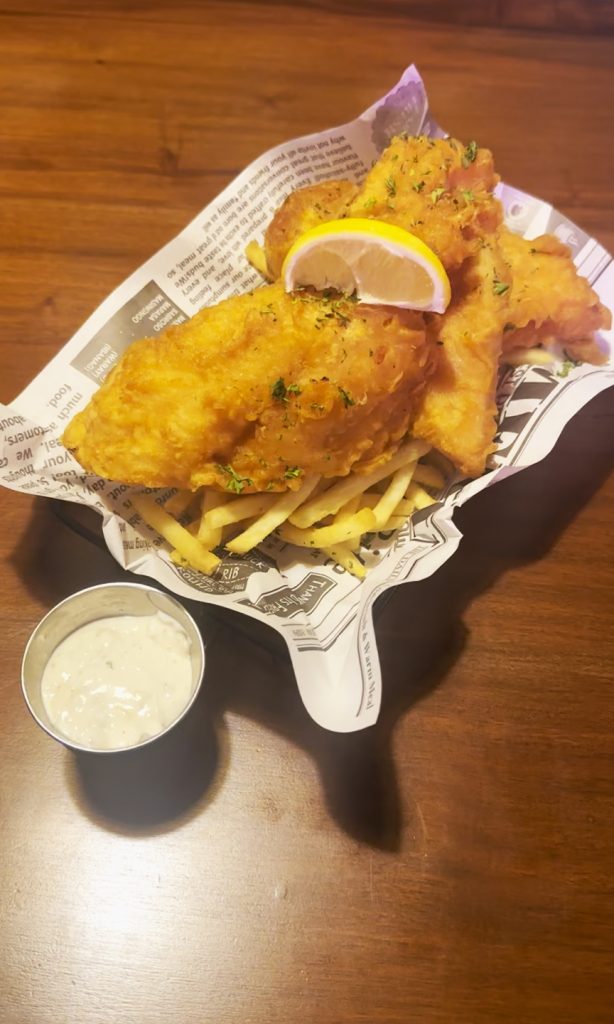
- The Fish and Chips (₱300) was actually good, comparative to those from delis in – say – some suburb in Australia. The fish wasn’t malansa, was properly battered, and was well cooked. The chips – or fries – naman were of good quality, not disintegrating to the touch.
- The Meatballs Tomato (₱250) was so-so; that is, the meatballs tasted nice, but the pasta was just too sweet. Ganito: If you added more pasta, the sweetness of the sauce would still overhwlem.
- The Signature Ribeye Steak (₱550) was a bit small, though not surprising considering the asking price. Ordered MR, it was properly done, with the meat still juicy. You don’t get a lot of accompanying veggies; though the eggs we ordered in place of the potatoes were well done.
- The Surf and Turf (₱650) was basically a Ribeye Steak… with grilled shrimps. For both steaks, if there’s a major comment, it’s the lack of seasoning. Yeah, you can just add salt and pepper; but it tastes different when meat is seasoned before or during cooking since nanunuot ang lasa. The mashed potato was too margarine-y, and so was so-so. The shrimps were good even if they were somewhat small.
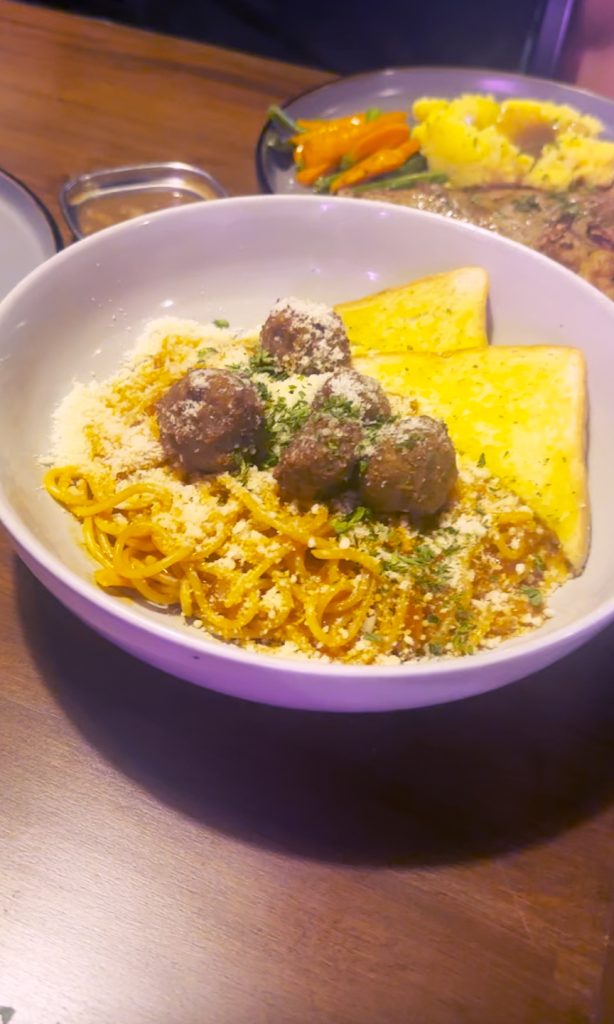
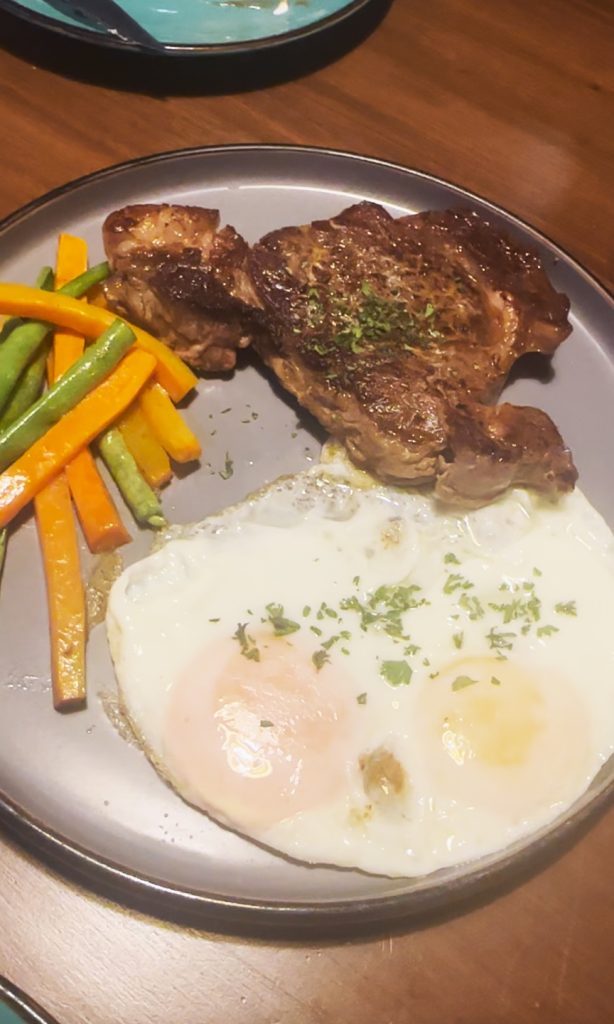
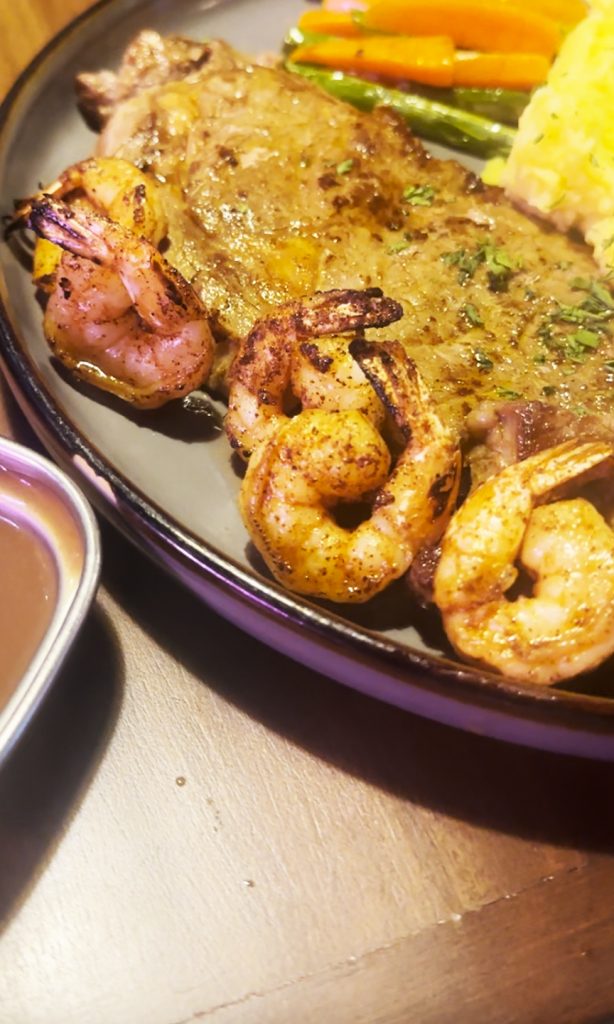










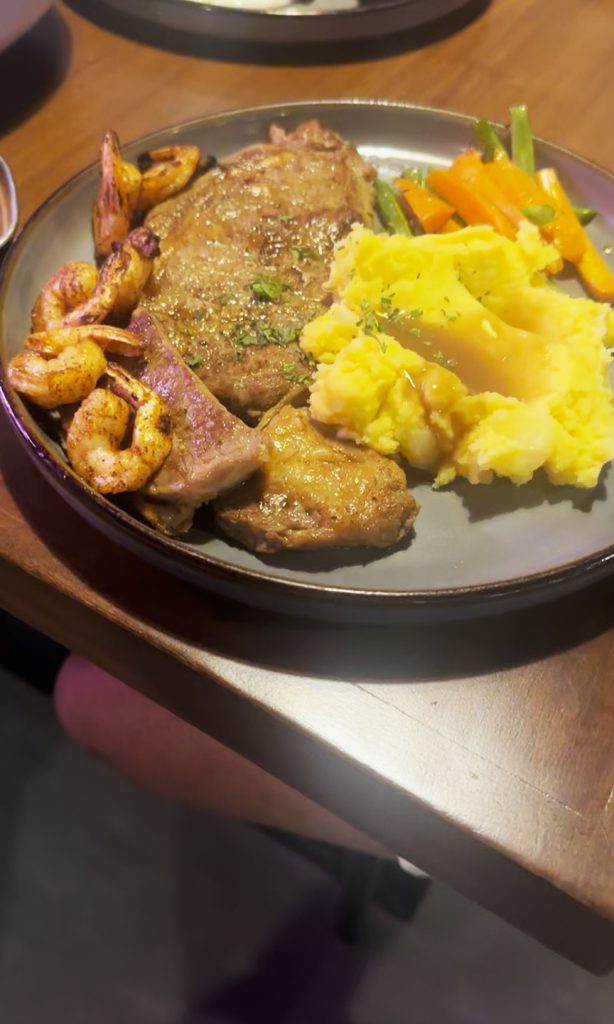




Is it worth to dayo, to target Project Steak? If you’re nearby and are looking for affordable steaks, perhaps. The ambiance is good, the offerings are presented well (check the plating!), and so on. But if it’s too far for you, and if there are other options for the same price wherever you may be, stay there na lang. That way, walang sisi.
Otherwise, join us as we look for more lafang venues.
Project Steak is located along Doña Remedios Trinidad Hwy, Baliuag, Bulacan. For more information, contact 0939 708 7839 or 0923 631 2559.
Travel
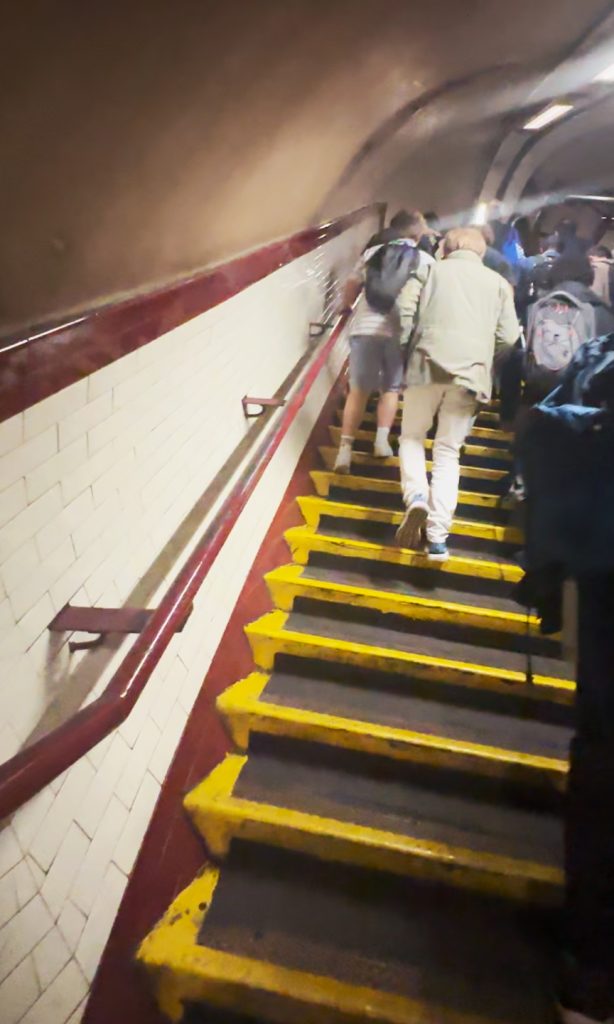
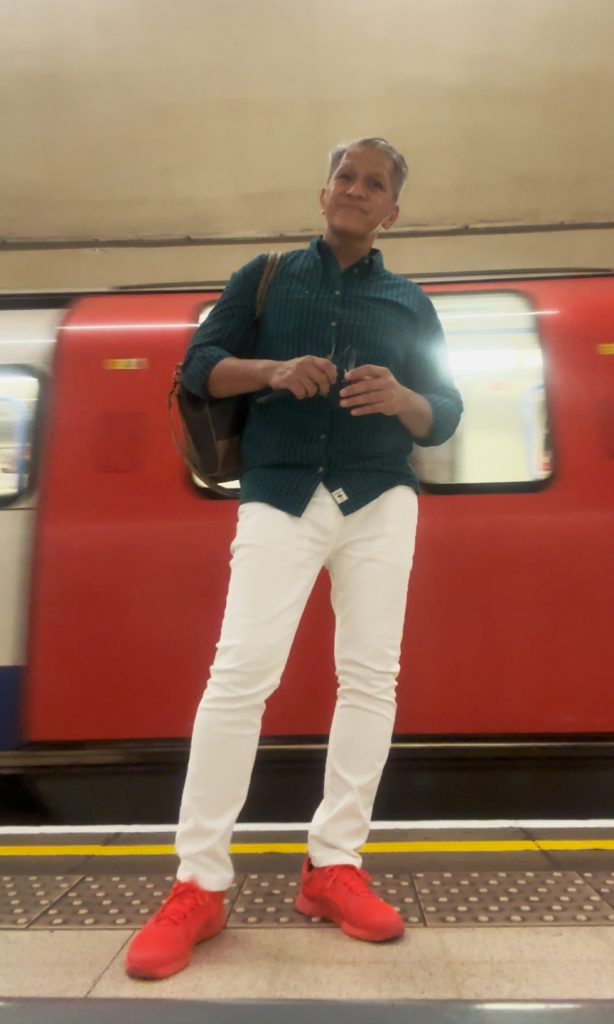
Checking the London Underground
UK’s London Underground serves millions every day, an example of a working train system (that we do not have in the Philippines). Sadly, 1 in 5 LGBTQIA+ travelers experience crime while using it, and 65% did not merit support from bystanders.
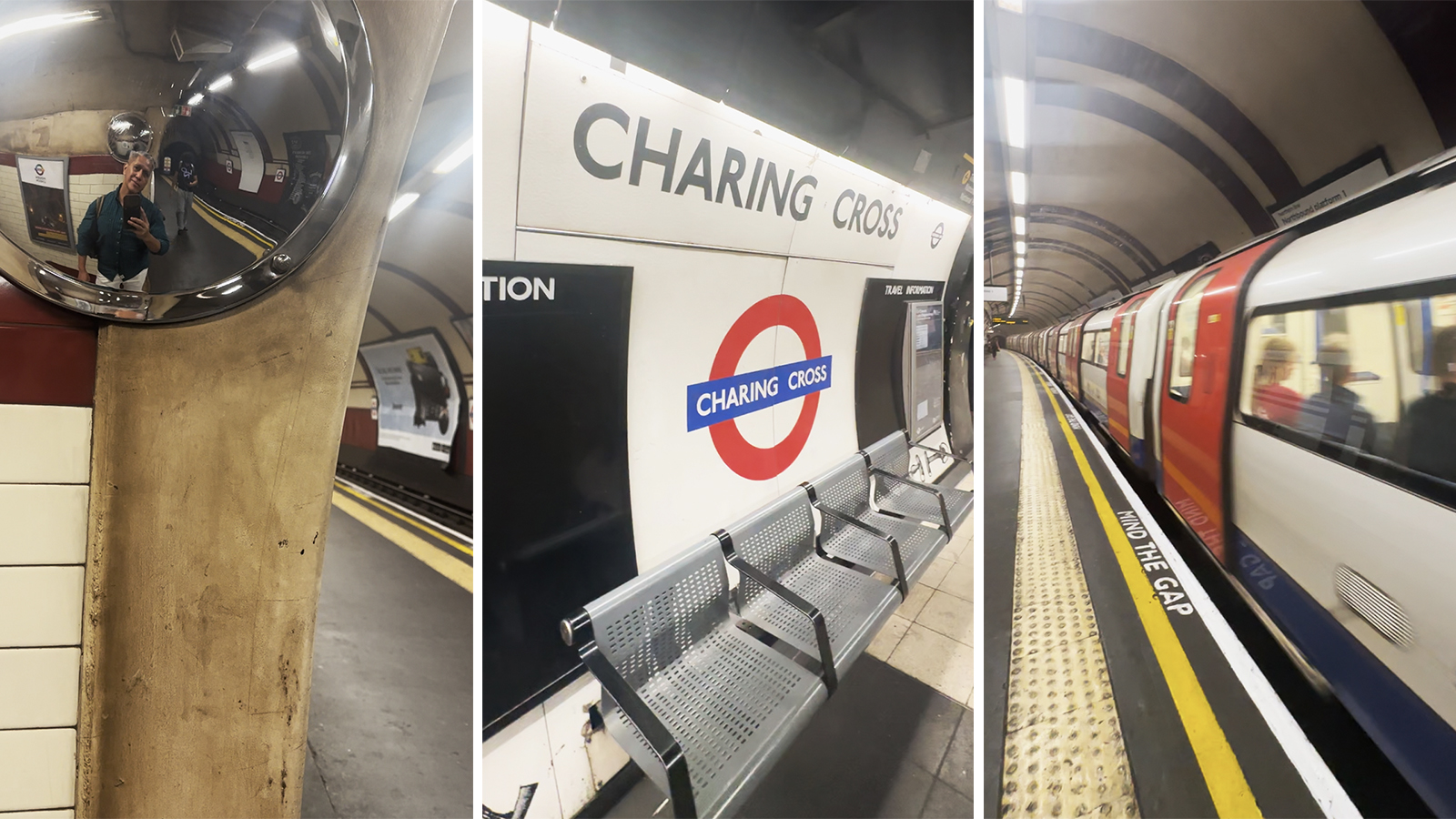

One way for Filipinos who are able to travel overseas can tell how bad our public transport system is, is by comparing the trains. We were invaded by White people in 1521, but – even now – we still only have three train lines.
@outragemag Check #LondonUnderground #trains in #London, aware it could be unsafe for #LGBT ♬ original sound – Outrage Magazine
UK, as an example, has the London Underground. Managed by Transport for London, this started in 1863 as the world’s first underground passenger railway. It now has 11 lines with 250 miles (400 kilometers) of track, with its 272 stations serving around five million passengers every day.
This isn’t a perfect system. Obviously, this is London-centric. It only serves the Greater London area, and some parts of the adjacent counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England. This is like saying na wala ngang LRT or MRT sa Bulacan o Cavite o Antipolo eh, and this lack highlights the exclusion of those also in need of proper public transport.
Looking at London’s train system through the LGBTQIA+ lens is actually disheartening… particularly if we talk not only about possibly meeting booking while riding trains. In 2023, London TravelWatch released a report that revealed that when LGBTQIA+ people used public transport:
- One in five (21%) experienced hate crime in the past year while travelling on public transport in London
- Four in five (82%) respondents changed their behavior or appearance to ‘fit in’ so they avoid abuse or harassment when travelling
- 65% of those who experienced abuse or harm when travelling in London said bystanders witnessed the incident but did not intervene
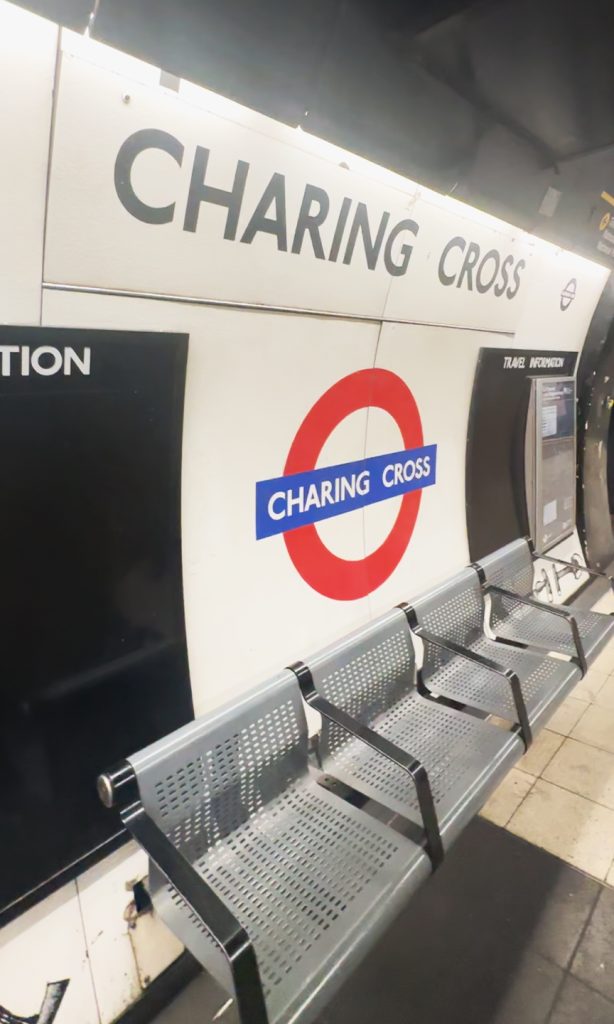
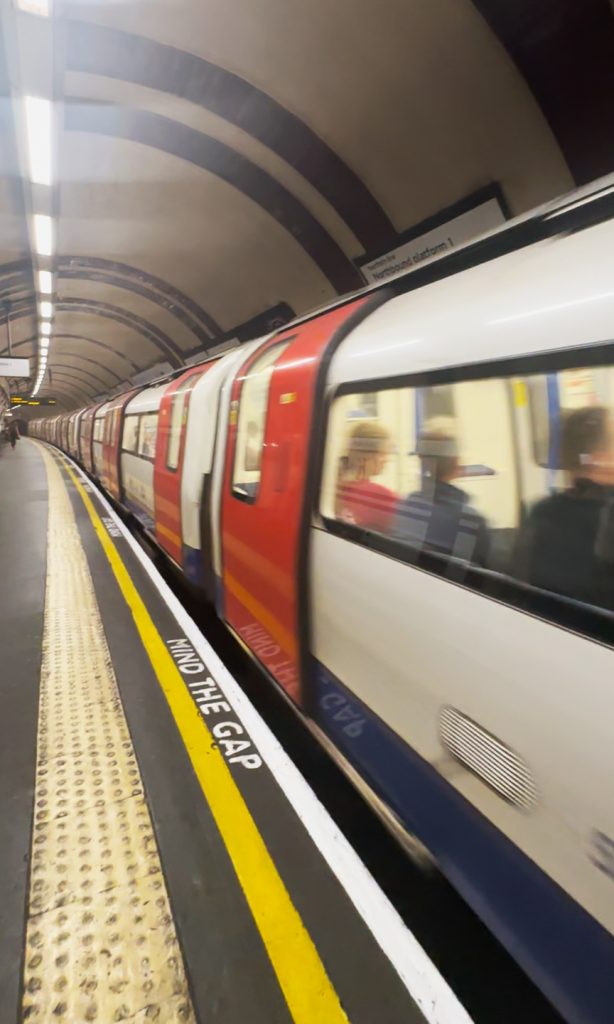
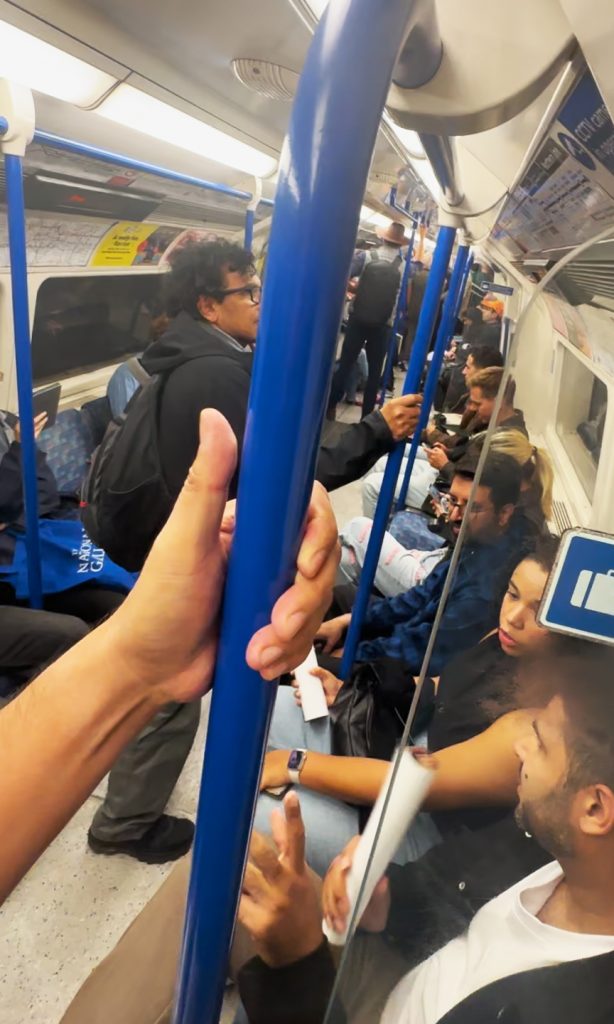







Lesson learned lang din: that even in spaces that better people’s lives, like a working train system, there are minority sectors that could be disadvantaged. And so this must always be considered to make sure all spaces are truly inclusive.
But off we go for more LGBTQIA+ rampa…
-

 Product Showcase3 weeks ago
Product Showcase3 weeks agoManulife Philippines ‘Time to MOVE’ symposium focuses on health and longevity
-

 NewsMakers1 week ago
NewsMakers1 week agoMillennials and Gen Zs prioritize health, purpose, financial independence, but health and wellness gaps persist
-

 Product Showcase1 week ago
Product Showcase1 week agoAIA Philippines CEO named Executive Champion of the Year in Asia
-

 Travel4 weeks ago
Travel4 weeks agoSteak-hunting in Bulacan? We ended up in Project Steak
-

 Destinations2 weeks ago
Destinations2 weeks agoChecking religious expression at Montemaria in Batangas
-

 Product Showcase1 week ago
Product Showcase1 week agoKorean brand Wells showcases 23 years of engineering innovation
-

 Destinations3 weeks ago
Destinations3 weeks agoBeach-hunting led to Malabrigo Beach
-

 Destinations3 days ago
Destinations3 days agoChecking out Street Halo-Halo Milky Ice
















